Consensus under sensor bias
Link to Report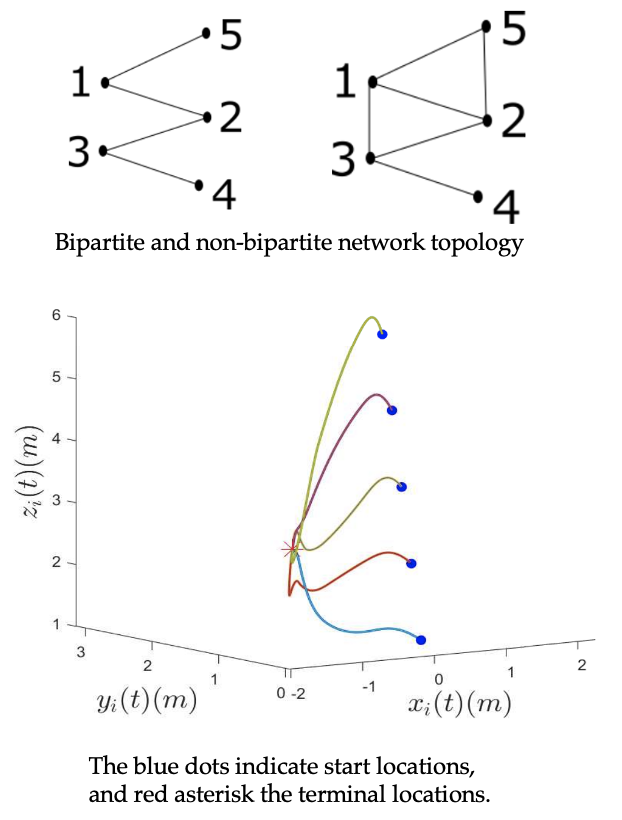
While adaptive control algorithms for disturbances and stochastic errors with upper bounds have been extensively studied, we delve into uncharted territory—consensus amidst measurement errors with unknown bounds. Traditional strategies for handling disturbances fall short in the face of measurement errors, as these errors scale with control gain, unlike external disturbances.
We develop an adaptive distributed control law using Lyapunov methods for consensus of networked double integrator systems [Paper]. The agents measure relative positions over a time-varying, undirected graph with an unknown and constant sensor bias corrupting the measurements. Our approach ensures that position consensus is achieved exponentially in addition to accurate individual bias estimation. We leverage recent advances in collective initial excitation based results in adaptive estimation and develop conditions connecting bipartite graphs and collective initial excitation. We demonstrate our algorithms in simulations on a network of double integrators with both Biartite and non-Bipartite local communication network topology and biased measurements.
